+91 9310434361
Enquiry Us
Cardiology
Angioplasty Surgery
Angioplasty Surgery through ALAAFIYAH CARE is affordable through our partnerships with state of the art hospitals in India. Medically trained case managers provide patient advocacy to ensure you receive the best medical care available for your procedure. Hospitals, officially recognized accreditation agencies such as JCAHO and the Joint Commission International (JCI), are thoroughly investigated prior to selection. Your procedure, including travel to and from the destination hospital, is managed by registered nurses from beginning to conclusion, guaranteeing you the optimum experience.
...What Is Angioplasty?
Coronary Angioplasty is a procedure that opens blocked arteries and allows blood to flow to your heart muscle. Angioplasty is not surgery. It opens a clogged coronary artery by inflating a tiny balloon in it.
Why is Angioplasty Done?
The arteries that bring blood to the heart muscle (coronary arteries) can become clogged by plaque (a build-up of fat, cholesterol and other substances). This can slow or stop blood flow through the heart’s blood vessels, leading to chest pain or a heart attack. Increasing blood flow to the heart muscle can relieve chest pain and reduce the risk of heart attack. You may be a good candidate for an angioplasty if:
- Your blockage is small
- Your blockage can be reached by angioplasty
- The artery affected isn’t the main vessel supplying blood to the left side of your heart
- You don’t have heart failure
If the main artery supplying the left side of your heart is narrowed, if your heart muscle is weak or if you have small, diffusely diseased blood vessels, then coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) may be a better option. In addition, if you have diabetes and multiple blockages, your doctor may suggest coronary artery bypass surgery. The decision of angioplasty versus bypass surgery will depend on the details of your heart disease and overall medical condition.
Angioplasty Preparation
To prepare for angioplasty, we require detailed medical information in the form of a medical questionnaire, ECG, Pulmonary tests and blood work. In some cases an Angiogram is required. All of this information will allow the doctors that we work with to determine your eligibility for the angioplasty procedure. Your doctor will give you specific instructions about any dietary changes or activity restrictions you should follow before surgery. As part of the pre-surgery tests done at our partner hospitals you will again receive chest X-rays, blood tests, an electrocardiogram and a coronary angiogram, which is a special type of X-ray procedure that uses dye to visualize the arteries that feed your heart.
How is Angioplasty Done?
General anesthesia isn’t needed, so you’re awake during the procedure. The doctor threads a thin tube through a blood vessel in the arm or groin up to the involved site in the artery. The tube has a tiny balloon on the end. When the tube is in place, the doctor inflates the balloon to push the plaque outward against the wall of the artery. This widens the artery and restores blood flow. Angioplasty is usually combined with implantation of a small metal coil called a stent in the clogged artery to help prop it open and decrease the chance of it narrowing again (restenosis). The stent looks like a very tiny coil of wire mesh. Stents can be coated with medication that’s slowly released to help prevent arteries from re-clogging. These coated stents are called drug-eluting stents, in contrast to no coated versions, which are called “bare-metal” stents. The entire angioplasty procedure can take 30 minutes to several hours
Angioplasty Recovery
You’ll remain hospitalized from 2 to 5 days while your heart is monitored and your vital signs are checked frequently. Your doctor will likely prescribe medications (anticoagulants) to prevent blood clots, relax your arteries and protect against coronary spasms. The hospital stay in our partner hospitals is much longer than what is provided in the INDIA and gives your doctor adequate time to monitor your recovery. You should be able to return to work or your normal routine the week after angioplasty
What about Alternatives to Angioplasty?
If the main artery supplying the left side of your heart is narrowed, if your heart muscle is weak or if you have small, diffusely diseased blood vessels, then coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) may be a better option. In addition, if you have diabetes and multiple blockages, your doctor may suggest coronary artery bypass surgery. The decision of angioplasty versus bypass surgery will depend on the details of your heart disease and overall medical condition.
Heart Bypass Surgery
Heart Bypass Surgery, with the support of ALAAFIYAH CARE, is accessible at State of the Art hospitals in the India, Malaysia & Turkey. We generally choose medical facilities certified by JCAHO or the Joint Commission International (JCI) for partnerships. In addition, the international hospitals work in co-operation with medical facilities. Our medically educated case managers are trained to facilitate your treatment with a personal approach appropriate for your specific circumstances.
...What is Heart Bypass Surgery?
Heart Bypass Surgery, also known as Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery, sometimes called CABG (cabbage), or simply “bypass surgery”, is a common procedure used to divert blood around clogged arteries in the heart. Coronary bypass surgery remains one of the gold standard surgical treatments for coronary artery disease. Success rates of an astonishing 99.8% are achieved with one of our partner hospitals.
Why is CABG Surgery Done
The arteries that bring blood to the heart muscle (coronary arteries) can become clogged by plaque (a buildup of fat, cholesterol and other substances).
This can slow or stop blood flow through the heart’s blood vessels, leading to chest pain or a heart attack. Increasing blood flow to the heart muscle can relieve chest pain and reduce the risk of heart attack.
Heart Bypass Preparation
To prepare for coronary bypass surgery, we require detailed medical information in the form of a medical questionnaire, ECG, Pulmonary tests and blood work. In some cases an Angiogram is required. All of this information will allow the doctors that we work with to determine your eligibility for the procedure.
Your doctor will give you specific instructions about any dietary changes or activity restrictions you should follow before surgery. As part of the pre-surgery tests done at our partner hospitals, you will again receive chest X-rays, blood tests, an electrocardiogram and a coronary angiogram, which is a special type of X-ray procedure that uses dye to visualize the arteries that feed your heart
How is Heart Bypass Surgery Done?
The surgeon makes an incision down the center of the chest, along the breastbone. The rib cage is spread open to expose the heart. After the chest is opened, the heart is stopped and a heart-lung machine takes over blood circulation to the body.
urgeons take a segment of a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body and make a detour around the blocked part of the coronary artery. A patient may undergo one, two, three or more bypass grafts, depending on how many coronary arteries are blocked. New procedures have been that may reduce the need for large incisions or a heart-lung machine: Off-pump or beating-heart surgery.
This procedure allows surgery to be done on the still-beating heart using special equipment to stabilize or quiet the area of the heart the surgeon is working on. This type of surgery is challenging because the heart is still moving. Because of this, it’s not an option for everyone.
Minimally invasive surgery. In this procedure, a surgeon performs coronary bypass through several smaller incisions in the chest. This technique is usually used only when certain conditions exist. If multiple coronary arteries need to be worked on, it’s best to use a conventional approach. Variations of minimally invasive surgery may be called port-access or keyhole surgery.
Heart Bypass Surgery Recovery
After surgery, the patient is moved to a hospital bed in the cardiac surgical intensive care unit. Heart rate and blood pressure monitoring devices continuously monitor the patient for 12 to 24 hours. Family members can visit periodically. Medications that regulate circulation and blood pressure may be given through the I.V. (intravenously).
A breathing tube (endotracheal tube) will stay in place until the physicians are confident that the patient is awake and ready to breathe comfortably on his or her own. The patient may feel groggy and disoriented, and sites of incisions may be sore. Painkillers are given as needed.
Patients usually stay in our partner hospitals for about one week or longer after surgery. This time is much longer than what is normally provided, giving your doctor adequate time to monitor your recovery. During this time, some tests will be done to assess and monitor the patient’s condition. After release from the hospital, the patient may experience side effects such as:
- Loss of appetite, constipation
- Swelling in the area from which the segment of blood vessel was removed
- Fatigue, mood swings, feelings of depression, difficulty sleeping
- Muscle pain or tightness in the shoulders and upper back
Many of these side effects usually disappear in four to six weeks, but a full recovery may take a few months or more. The patient is usually enrolled in a physician-supervised program of cardiac rehabilitation. This program teaches stress management techniques and other important lessons (e.g., about diet and exercise) and helps people rebuild their strength and confidence.
Patients are often advised to eat less fat and cholesterol and to walk or do other physical activity to help regain strength. Doctors also often recommend following a home routine of increasing activity- doing light housework, going out, visiting friends, climbing stairs.
The goal is to return to a normal, active lifestyle. Most people with sedentary office jobs can return to work in four to six weeks. Those with physically demanding jobs will have to wait longer. In some cases they may have to find other employment.
What About Alternatives to Coronary Artery Bypass?
In some patients, alternative treatment of coronary artery disease includes medical therapy with specific medication or non-surgical treatment such as balloon angioplasty, laser angioplasty, stents or atherectomy (plaque removal). Your physician (cardiologist) will help decide which treatment is best for you.
Heart Valve Repair Surgery
Heart Valve Repair through ALAAFIYAH CARE is affordable through our partnerships with state-of-the-art hospitals. Medically trained case managers provide patient advocacy to ensure you receive the best medical care available for your procedure. Hospitals, officially recognized accreditation agencies such as JCAHO and the Joint Commission International (JCI), are thoroughly investigated prior to selection. Your procedure, including travel to and from the destination hospital, is managed by registered nurses from beginning to conclusion, guaranteeing you the optimum experience.
... Most importantly, we provide you with a personal touch from start until the end even after your return home.What is Heart Valve Repair?
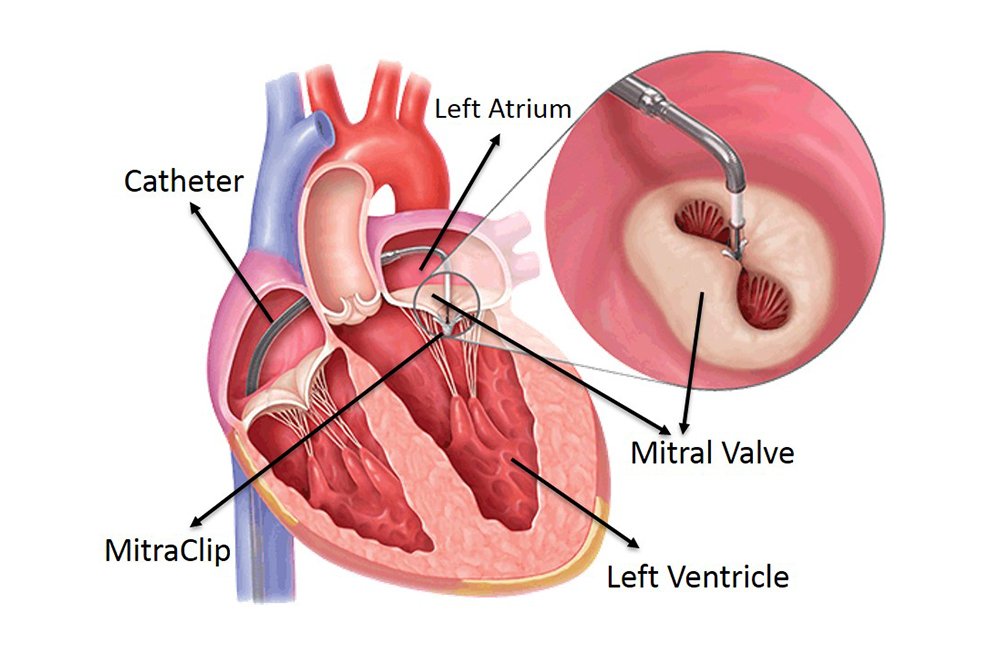
Heart valve surgery is needed when a heart valve doesn’t work right. A valve may not open all the way or a valve may have problems closing. If this happens, blood doesn’t move through the heart’s chambers the way it should. If a valve doesn’t open all the way, less blood moves through to the next chamber. If a valve doesn’t close tightly, blood may leak backward. These problems may mean that the heart must work harder to pump the same amount of blood or blood may back up in the lungs or body because it’s not moving through the heart as it should. During heart valve replacement, one or more valves are replaced. Repair means that the valve is mended to help it work better. Replacement means your diseased valve is removed and a new valve is inserted in its place. Whether a valve will be repaired or replaced can only be decided once surgery has begun.
Heart Valve Repair Preparation
To prepare for heart valve repair surgery, we require detailed medical information in the form of a medical questionnaire, ECG, Pulmonary tests and blood work. In some cases, an Angiogram is required. All of this information will allow the doctors that we work with to determine your eligibility for the procedure. Your doctor abroad will give you specific instructions about any dietary changes or activity restrictions you should follow before surgery. As part of the pre-surgery tests done at our partner hospitals abroad, you will again receive chest X-rays, blood tests, an electrocardiogram and a coronary angiogram, which is a special type of X-ray procedure that uses dye to visualize the arteries that feed your heart.
How is Heart Valve Repair Done?
During valve repair, a ring may be sewn around the opening of the valve to tighten it. Other parts of the valve may be cut, shortened, separated, or made stronger to help the valve open and close right.
Traditional Heart Valve Repair
During traditional heart valve surgery, a surgeon will make an incision down the center of your sternum (breastbone) to get direct access to your heart. The surgeon then repairs or replaces your abnormal heart valve or valves.
Minimally Invasive Heart Valve Repair
Minimally invasive surgery is a type of heart valve replacement performed through smaller incisions. This type of surgery reduces blood loss, trauma, and length of hospital stay. Heart valve surgery is the most common minimally invasive procedure. Your surgeon will review your diagnostic tests prior to your surgery to see if you are a candidate for minimally invasive valve surgery.
Heart Valve Repair Recovery
You’ll remain hospitalized for about 10 days while your heart is monitored and your vital signs are checked frequently. Your doctor will likely prescribe medications (anticoagulants) to prevent blood clots, relax your arteries, and protect against coronary spasms. The hospital stay in our partner hospitals is much longer than what is provided and gives your doctor adequate time to monitor your recovery.
Your doctor will advise you to walk or to do other physical activities, increasing gradually in order to regain your strength and return to a normal, active lifestyle. Most individuals who have sedentary jobs can return to work in four to six weeks. Those who have physically demanding jobs will have to wait longer. Additionally, your doctor will not want you to drive a car for six weeks.
...Heart Valve Replacement Treatments
Heart valve surgery is needed when a heart valve doesn’t work right. A valve may not open all the way or a valve may have problems closing. If this happens, blood doesn’t move through the heart’s chambers the way it should. If a valve doesn’t open all the way, less blood moves through to the next chamber. If a valve doesn’t close tightly, blood may leak backward. These problems may mean that the heart must work harder to pump the same amount of blood or blood may back up in the lungs or body because it’s not moving through the heart as it should. During heart valve replacement, one or more valves are replaced.
Thus there are several different types of heart valve replacement procedures, such as aortic valve replacement, mitral valve replacement, and others.
Repair means that the valve is mended to help it work better. Replacement means your diseased valve is removed and a new valve is inserted in its place. Whether a valve will be repaired or replaced can only be decided once surgery has begun.
Heart Valve Replacement Preparation
To prepare for coronary bypass surgery, we require detailed medical information in the form of a medical questionnaire, ECG, Pulmonary tests and blood work. In some cases, an Angiogram is required. All of this information will allow the doctors that we work with to determine your eligibility for the procedure.
Your doctor will give you specific instructions about any dietary changes or activity restrictions you should follow before surgery. As part of the pre-surgery tests done at our partner hospitals, you will again receive chest X-rays, blood tests, an electrocardiogram and a coronary angiogram, which is a special type of X-ray procedure that uses dye to visualize the arteries that feed your heart.
How is Heart Valve Replacement Done?
Traditional Heart Valve Replacement
During traditional heart valve surgery, a surgeon will make an incision down the center of your sternum (breastbone) to get direct access to your heart. The surgeon then repairs or replaces your abnormal heart valve or valves.
Minimally Invasive Heart Valve Replacement
Minimally invasive surgery is a type of heart valve replacement performed through smaller incisions. This type of surgery reduces blood loss, trauma, and length of hospital stay. Heart valve surgery is the most common minimally invasive procedure. Your surgeon will review your diagnostic tests prior to your surgery to see if you are a candidate for minimally invasive valve surgery.
Heart Valve Prostheses
Two kinds of prosthetic heart valves are available:
- Mechanical valves are created from man-made materials. Lifetime therapy with an anticoagulant (sometimes called a “blood thinner”) is needed when these types of valves are used. This medication prevents blood clots from forming on or around the valve.
- Biological (tissue) valves are taken from pig, cow, or human donors. These valves don’t last as long as mechanical valves. But when tissue valves are used, long-term use of an anticoagulant often isn’t needed.
Heart Valve Replacement Recovery
You’ll remain hospitalized for about 10 days while your heart is monitored and your vital signs are checked frequently. Your doctor will likely prescribe medications (anticoagulants) to prevent blood clots, relax your arteries, and protect against coronary spasms. The hospital stay in our hospitals is much longer than what is normally provided, which gives your doctor adequate time to monitor your recovery.
Your doctor will advise you to walk or to do other physical activities, increasing gradually in order to regain your strength and return to a normal, active lifestyle. Most individuals who have sedentary jobs can return to work in four to six weeks. Those who have physically demanding jobs will have to wait longer. Additionally, your doctor will not want you to drive a car for six weeks.
Heart Valve Replacement at low cost and high quality is now within reach through ALAAFIYAH CARE. Our nurses arrange all aspects of your treatment and will act as your patient advocate.
Most importantly, we provide you with a personal touch from start until well after your procedure is completed.
We also provide information and all the logistic support.
High Quality Pacemaker Surgery
Pacemaker Surgery through ALAAFIYAH CARE is a unique approach to first-class medical care. Our association with high-quality hospitals makes surgical procedures at reasonable rates possible for everyone. Our case managers, all medically trained, organize every aspect of your procedure and have helped many patients receive medical intervention within a reasonable time.
...What is a Pacemaker?
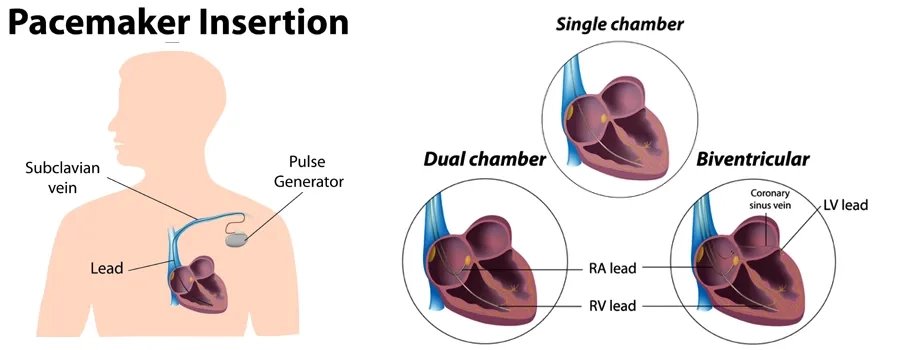
Pacemakers are implanted in patients with slow heart rhythms, heart failure, or fainting episodes. A pacemaker is a small device that regulates your heartbeat with electrical pulses. Pacemakers have two components called the “leads” and “pulse generator”. The pulse generator is placed just under your skin and has a battery and miniscule computer. The leads are inserted into your veins and heart muscle. They carry the electrical impulses to your heart.
There are three types of pacemakers:
- Single Chamber, which has one lead
- Dual Chamber, which has two leads
- Biventricular, which has three leads
Which pacemaker your doctor recommends will be based on your medical condition?
A pacemaker implant procedure through ALAAFIYAH CARE may save you thousands of dollars for the procedure.
The Pacemaker Implant
A pacemaker implant is performed in the hospital and, dependent on the type of surgery, lasts between 2 and 5 hours.
There are two types of implantation methods:
- Endocardial approach and epicardial approach. The endocardial approach is the most common.
- Once again, you should consult with your doctor as to the best approach for your circumstances.
- An intravenous line will be inserted into your hand or arm. You will be given medication through the IV to make you relaxed and drowsy. You will be awake during the procedure, but should feel no pain. If you do have pain, inform the nurse immediately.
You will be connected to monitors, which record your blood pressure and heart rate during the implantation.
After your chest has been shaved and cleansed, the doctor will give you a local anesthetic where the incision will be located. Once the incision has been made, the doctor will insert the leads into a vein and guide them into your heart muscle with the assistance of a special x-ray machine. The leads are then tested to ensure they are working properly.
Next, the doctor will connect the leads to the pulse generator and place the generator into the incision just underneath your skin. The incision is then closed.
Risks associated with pacemaker surgery are internal bleeding, infection, embolism, heart perforation, and scarring. Discuss the risks of pacemaker implantation with your medical specialist to make certain you are fully aware of the possible hazards.
Pacemaker Preparation
You will have cardiac testing prior to your surgery. These may include an electrocardiogram, electrophysiological study, x-rays, and blood tests your doctor will review your current medications. Be sure he or she has a full listing of every medication and the dosage you take. Your doctor may ask you to stop taking certain medications a number of days prior to the implant.
If you are diabetic, you should discuss whether adjustments to your insulin schedule during your hospital procedure are needed.
You will likely be requested to stop eating or drinking after midnight the evening prior to your procedures. Your doctor may also ask you to consume only clear fluids for one or more days in advance of the implant.
If you smoke, it is advisable you stop 6 to 8 weeks before the procedure to reduce the risk of breathing problems during the procedure and delayed wound healing.
Pacemaker Recovery
You will stay in the hospital for monitoring of your heart rate and functioning of the pacemaker.
You may notice bruising, pain, and tenderness around the incision site for the first few weeks after the implant. This is usually mild. Once you have been released from the hospital, your activities may be restricted for the first six weeks. You may possibly need to pace yourself so you do not become overtired.
Strenuous activities and your return to work can be resumed as advised by your doctor.
Certain physical movements, such as lifting, pushing, or pulling heavy objects, should be avoided.
In addition, you should not lift your arms above shoulder height if possible.
You may have to limit your use of electrical devices, such as cell phones, iPods, and appliances. Your doctor can advise you about necessary precautions.
You will see your specialist for follow-ups on a regular basis for adjustments and a battery check. A regular schedule of check-ups will help your pacemaker last longer.
Pacemaker Surgery at low cost and high quality is now within reach through ALAAFIYAH CARE. Our nurses arrange all aspects of your treatment and will act as your patient advocate.
Most importantly, we provide you with a personal touch from start until well after your procedure is completed.
We also provide information and all the logistic support.
RF Ablation Heart Treatment
RF Ablation treatment through ALAAFIYAH CARE is within your financial means. Our registered nurses make all arrangements necessary for the success of your procedure. Our services carry the promise of quality medical care with individual attention to your needs.
...What is Radiofrequency Ablation?
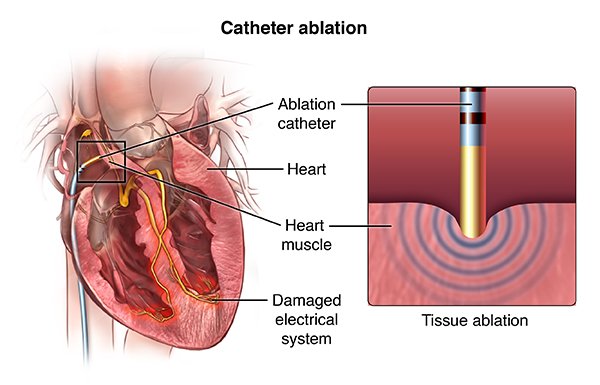
Radiofrequency Ablation heart treatment is a nonsurgical procedure used to treat some types of rapid heart beating. It is most often used to treat supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. These are rapid, uncoordinated heartbeats. They start in the heart’s upper chambers (atria) or middle region (AV node or the very beginning portion of the heart’s electrical system).
Cardiac Radiofrequency Ablation: The Procedure
A physician guides a catheter with an electrode at its tip to the area of heart muscle where there’s an accessory (extra) pathway. The catheter is guided with real-time, moving X-rays (fluoroscopy) displayed on a video screen.
The procedure helps the doctor place the catheter at the exact site inside the heart where cells give off the electrical signals that stimulate the abnormal heart rhythm. Then a mild, painless radiofrequency energy (similar to microwave heat) is transmitted to the pathway. This destroys carefully selected heart muscle cells in a very small area (about 1/5 of an inch). That stops the area from conducting the extra impulses that caused the rapid heartbeats.
How common is this Procedure?
RF ablation heart therapy (also called cardiac ablation) is widely used. It’s the preferred treatment for many types of rapid heartbeats. Radio frequency ablation heart treatment has a success rate of over 90 percent and a low risk of complications. Patients who have this done can resume normal activities in a few days. It causes little or no discomfort and is done under mild sedation with local anesthesia.
What are Cardiac Problems?
Cardiac problems refer to disorders, diseases, or malfunctioning of the heart and its supporting blood delivery system (the veins and arteries – blood vessels).
Types of Cardiac Problems
The Cardiac Problems are categorized into:
...- Electrical cardiac problems are a result of a defective electrical system which controls the heartbeat. This results in the heart beating significantly faster or abnormally slower. It also results in the heart beats becoming infrequent or unsteady. At times, serious irregular heartbeats (such as arrhythmia) are known to develop into severe heart problems, including cardiac arrest.
- Circulatory cardiac problems are related to the blood circulation system of the body. In this type of cardiac disorder, the patient suffers from high blood pressure and coronary artery disease (obstruction in passageways in the heart). These are known to result in stroke, heart attack, and even be fatal if left undiagnosed and untreated for long.
- Structural cardiac disorders affect the structure of the heart, including birth defects, cardiac muscle issues, or valve malfunctioning.
Types of Cardiac Treatments
There are a large variety of cardiac treatments available today. These are mostly surgical procedures (conventional and minimally invasive) that are aimed at treating the cause of the heart problems.
These are some of the most commonly performed cardiac treatment procedures:
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery
The CABG surgery is the most common treatment for circulatory cardiac disorders. As coronary heart disease is caused due to the accumulation of plaque (hardened waxy substance) inside the coronary arteries (blood vessel supplying blood to the heart) the CABG procedure aims to clear the obstruction.
Why Choose ALAAFIYAH CARE For Cardiac Treatments?
ALAAFIYAH CARE understands the emergency and the urgent need for medical attention required in cardiac cases. The company has ties with the most renowned and reliable hospitals from all over the world. This is an expansive global network of high-standard cardiac specialty hospitals at major international destinations. ALAAFIYA ensures the best, most efficient and affordable cardiac treatments in exotic locations, including Thailand, Malaysia, Turkey, and Dubai.
